The Lithium Triangle’s rise in the EV race
At a glance:
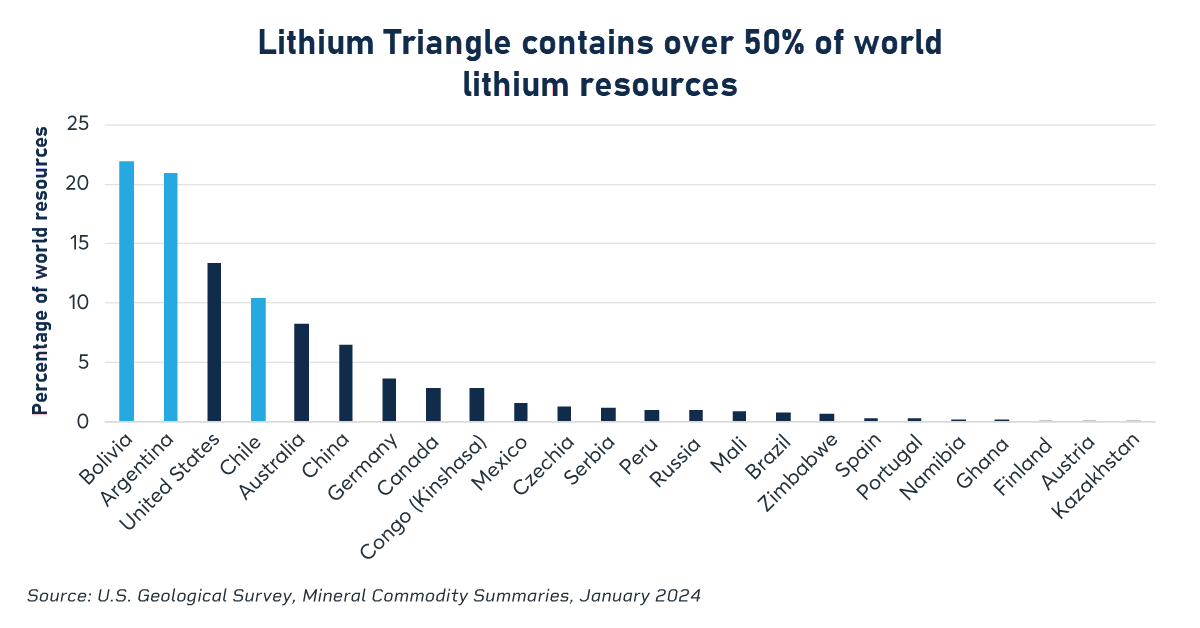
- Argentina, Chile and Bolivia make up the Lithium Triangle, which could eclipse China and Australia as the world’s top lithium maker.
- As the rush to mine the new “white gold” intensifies, Argentina is set to draw massive investments.
By Ivan Castano for CME Group
October 30, 2024

South America’s so-called Lithium Triangle is set to draw over $30 billion in about five years as a slew of Chinese, North American and Australian investors looks to seize coveted assets to supply the new ‘white gold’ powering electric vehicles (EVs), according to Gonzalo Mondaca, a senior researcher with Bolivian think tank Cedib, and Daniel Dreizzen, who runs Buenos Aires-based consultancy Aleph Energy and is Argentina’s former energy planning secretary.
The race to control nearly two-thirds of global lithium reserves held by Argentina, Bolivia and Chile, which together make up the Lithium Triangle), is heating up. Mondaca, Dreizzen and other analysts say these nations could surpass Australia and China as the world’s top producer of the increasingly popular metal in less than a decade.
Argentine drive
Between $10 billion and $20 billion is expected to pour into Argentina by 2029 as the owner of the world’s second-largest estimated reserves (22 million tons) looks to boost production to 380,000 annual tons of battery-grade lithium carbonate, up from 70,000 tons currently, according to Dreizzen.
He says at least six plants are currently under construction – owned by Arcadium Lithium, Australia’s Argosy Minerals, Chinese steel firm Zijing, Chinese lithium major Ganfeng, South Korea’s Posco and Chinese miner Tibet Summit Resources.
If construction is completed, the move could catapult Argentina to the world’s third largest producer in about five years, surpassing China and Chile.
Argentina’s lithium ambitions may not be enough to eclipse Australia as the planet’s top supplier of the lightweight metal, also used to make cellphones and laptops. Australia churned out 86,000 tons of the metal from its “hard rock” spodumene deposits last year, making up 47 percent of the global market.
In turn, the United States makes just 5,000 tons from a small plant in Silver Peak, Nevada, through Albemarle, the world’s largest lithium producer. Plans to utilize the nearby Thacker Pass mine – forecast to produce 66,000 tons, or enough lithium to power 800,000 electric cars – by 2027 could sharply boost that number.
Balancing policy
This summer, Argentina passed a law creating a new incentive regime for large investments (RIGI, by its Spanish acronym). The plan provides incentives for 30 years to mining, agribusiness, energy and other sectors investing at least $200 million in the country.
It also has the most “business-friendly” investor environment in the Triangle as Buenos Aires has handed control of the three lithium-rich regions of Jujuy, Catamarca and Salta to its governors which have prioritized foreign entities.
Lithium risk management needs grow
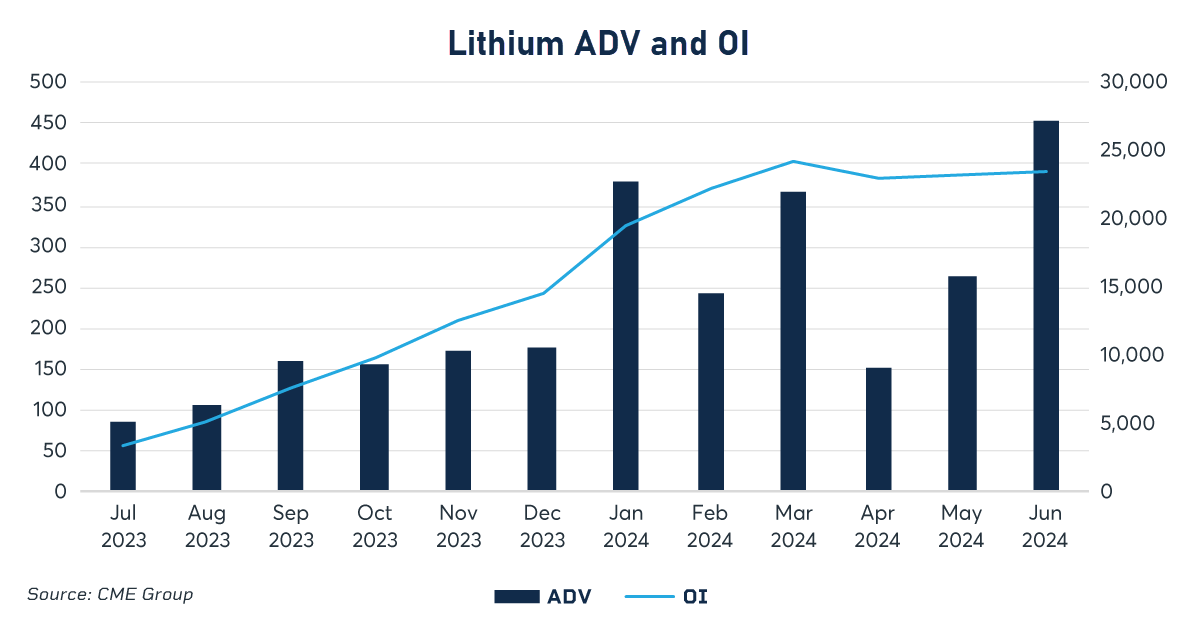
With the rising potential for lithium mining in South America comes price risk and the need to hedge exposure to a changing production environment. As a result, 498 tons of Lithium Hydroxide futures traded per day in June – an increase of over 1,541 percent from a year earlier as more participants are looking to trade Lithium Hydroxide futures to manage price risk.
The trend continued through July when CME Group’s two lithium futures contracts set records for open interest – the number of unsettled contracts – on back-to-back days to close the month.
“A key component of small-device batteries used in phones, cars and more, lithium demand is growing and creating an increased need to manage fluctuating price risk,” said Jin Hennig, CME Group managing director and global head of metals. “As a result, market participants are turning to our lithium futures market in record numbers, driving up both open interest and volume. In just the first half of 2024, trading in our Lithium Hydroxide futures contract has already surpassed full-year 2023 totals.”
Chilean nationalization
Chile recently announced a partial lithium nationalization, merging state-run copper maker Codelco and rival SQM to control 51 percent of projects in the country’s strategic salt flats. The action triggered a selloff in Chilean shares as some investors responded to the news. But others shrugged off the move.
Chinese car maker BYD, for instance, is moving forward with its plans to build a $290 million battery materials plant in the northern port city of Antofagasta, scheduled to come onstream in 2025. Texas-based EnergyX, meanwhile, is moving into the country to build a production pilot plant that will use its proprietary direct lithium extraction (DLE) technology.
“The government is not nationalizing all lithium,” says EnergyX’s founder Teague Egan. “They are actually opening their borders for more foreign investment. While the state is taking a majority share in the two top salars [salt flats], Atacama and Maricunga, they have opened up nearly 30 more salars for private company development.”
Chile is moving to bolster lithium production to 370,000 tons by 2030, up from 300,000 tons now, according to Telye Yurisch, chief investigator at environmental advocacy group Terram. This will happen if it can successfully auction 26 salars in the key Atacama region for which it has yet to unveil its future stakes, adding uncertainty to the process, he added.
Bolivian delays
Meanwhile Bolivia has been slow to ramp up production.
Despite holding the world’s largest estimated reserves of 23 million tons, it currently produces just 600 tons of lithium with plans to boost it to 15,000 tons by late 2024.
Last summer, Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) and rival CMOC announced plans to build two plants in the fabled Uyuni salt flats, a massive salt desert containing the reserves and a major tourist spot. The firms aimed to invest $1.4 billion, produce 100,000 tons by 2028 and export EV batteries by 2025. Simultaneously, China’s CITIC Guoan and Russia’s Rosatom also announced plans to produce 100,000 tons. President Luis Arce said the nation could draw over $9 billion in the process by 2028.
But the plans have not yet materialized.
“All of the timelines are delayed,” said Mondaca, as La Paz scrambles to carry out feasibility studies. This means Bolivia’s plan to elevate its lithium output and make batteries has become increasingly difficult to achieve.
In light of all the challenges, can the Triangle become a global lithium powerhouse, eventually beating Australia and China? Andy Leyland, co-founder of consulting company SC Insights which specializes in lithium-ion battery supply chains, said it’s possible.
“They could do it but only with Bolivia in the long-term,” he said. “It could take five to seven years but we will have to see the final numbers [as new projects break ground]” before drawing any conclusions.
The content is paid for and supplied by advertiser. The Washington Post was not involved in the creation of this content.
Content From
